NUCLEIC ACIDS
These
contain genetic information that each organism needs in order to know which
proteins to make. We will be concerned
with the relation of nucleic acids to protein structure. There are an infinite number of possible
protein structures and also many
different life forms. Each living
system must select which proteins to make for its own special needs and also
pass on this information to its off-spring.
We
will be concerned with structural
constraints in nucleic acids which allow for not just the storing of
genetic information but also allow the involvement of these acids in the
transmission of genetic information from molecule to molecule.
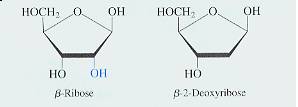
The four nucleotide building blocks for DNA and RNA are made from the following components. These are
phosphoric acid, the pentose sugars ribose and 2- deoxyribose
P R D
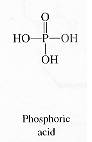
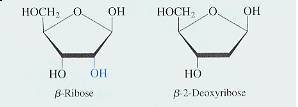
and the heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
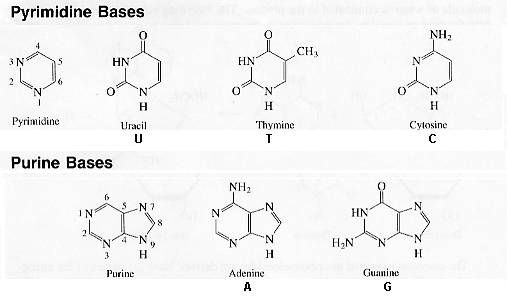
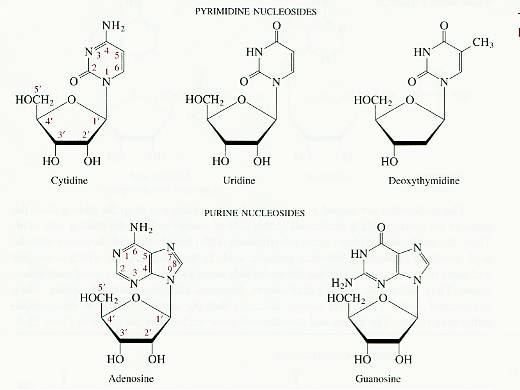
Pentose - base condensation reactions occur at the no.1 O-H
on the pentoses to the no.1 N-H of pyrimidine bases and the
no.9 N-H of the purine bases.
pentose + base à H2O + nucleoside
will give e. g., the following nucleoside products

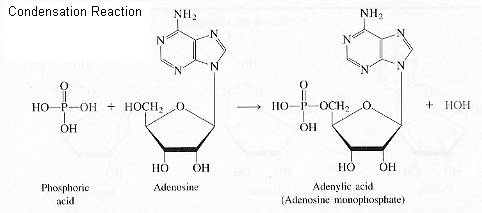
Condensation of phosphoric acid with the nucleoside at the pentose no. 5 –OH gives for example the nucleotide
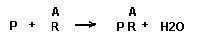
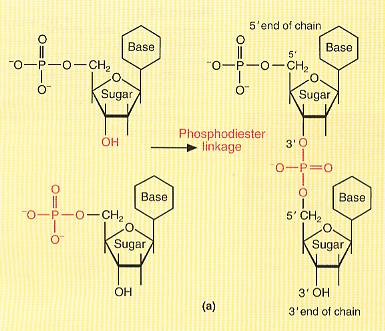
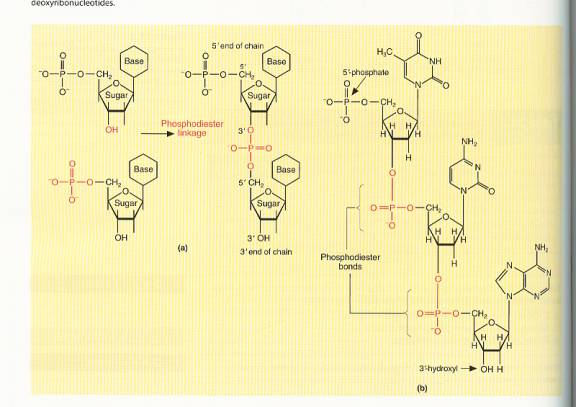
The 4 DNA nucleotides are building blocks that condense to form polynucleotides. The DNA molecule contains millions of nucleotides.
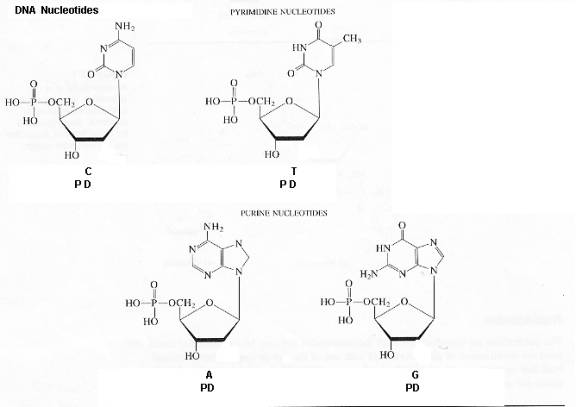
The condensations are
nucleotides à water + polynucleotide

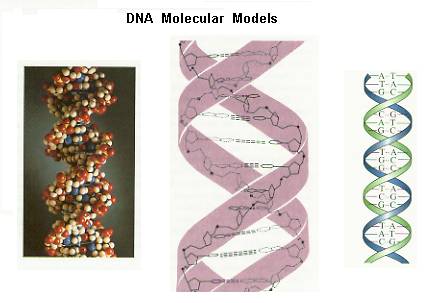
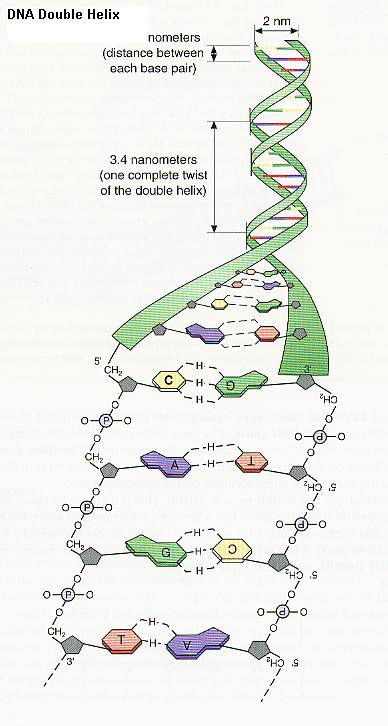
DNA double helix
Processes involving communication of genetic information from molecule to molecule:
Replication, Transcription, and Translation.